Diethyl carbonate is an organic carbonate ester with the molecular formula C5H10O3. Structurally, it consists of a central carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two ethoxy groups (–OCH2CH3), giving it the general structure of a symmetrical dialkyl carbonate. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a mild odor, low viscosity, and moderate solubility in water, while being miscible with most organic solvents.
Diethyl carbonate is primarily used as a reactive solvent and chemical intermediate in organic synthesis. Its carbonate functionality allows it to participate in transesterification reactions, transferring the carbonate group to alcohols or amines to produce dialkyl carbonates or carbamates. It is also employed in alkylation reactions as a source of the ethyl carbonate group in carboxylation or alkylation processes. Because of its relatively low toxicity and biodegradability, diethyl carbonate is considered a green reagent and has gained interest as a replacement for more hazardous alkylating agents such as phosgene or dimethyl sulfate.
In industrial chemistry, diethyl carbonate serves as a precursor in the synthesis of polycarbonates, polyurethanes, and other polymeric materials. It reacts with diols to form polycarbonate chains through transesterification, providing an alternative to phosgene-based polycarbonate production. Its use in polymer chemistry allows for the preparation of environmentally friendlier materials with reduced toxic byproducts.
Diethyl carbonate is also used as a solvent in lithium-ion batteries and other electrochemical applications. Its high dielectric constant and ability to dissolve lithium salts make it suitable as a component in electrolyte solutions, often combined with other carbonate solvents to optimize conductivity, viscosity, and electrochemical stability.
Synthetically, diethyl carbonate can be produced by phosgene-free methods such as the reaction of ethanol with urea, oxidative carbonylation of ethanol using carbon monoxide and oxygen, or transesterification of dimethyl carbonate with ethanol. These methods are preferred for industrial production due to safety and environmental considerations.
Overall, diethyl carbonate is a versatile and valuable organic carbonate, notable for its use as a green solvent, chemical intermediate, and polymer precursor. Its structure, featuring a central carbonate group flanked by two ethyl groups, underpins its reactivity in transesterification, alkylation, and polymerization reactions, while its physical properties make it useful in a range of industrial and laboratory applications.
References
2014. Stable Cycling of SiO2 Nanotubes as High-Performance Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Scientific Reports, 4.
DOI: 10.1038/srep04605
2012. Inexpensive method for producing macroporous silicon particulates (MPSPs) with pyrolyzed polyacrylonitrile for lithium ion batteries. Scientific Reports, 2.
DOI: 10.1038/srep00795
2005. Direct Yellow and Methylene Blue liquid-liquid extraction with alkylene carbonates. Chemosphere, 60(8).
DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.019
|
















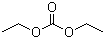

 GHS02;GHS07 WarningGHS02 Details
GHS02;GHS07 WarningGHS02 Details