Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Lavin Chemical (nantong) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13862887077 | |||
 |
lavin@lavinchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyrimidine compound >> Amine |
|---|---|
| Name | 4-(Dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine |
| Molecular Structure | 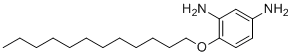 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H32N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 292.46 |
| CAS Registry Number | 141505-05-7 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1)N)N |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 443.5±25.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 222.0±16.8 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.529 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
4-(Dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine (CAS 141505-05-7) is an aromatic diamine in which a benzene ring substituted with two amino groups at the 1 and 3 positions also bears a long linear dodecyloxy (-O-C12H25) chain at the 4 position. Its molecular formula is C18H32N2O and the compound combines the reactive 1,3-phenylenediamine core with a flexible hydrophobic tail. The structural motif of an aromatic diamine with a long alkoxy substituent makes it significantly more soluble in organic media and can strongly influence the physical properties of materials derived from it. The chemistry of aromatic diamines such as benzene-1,3-diamine itself (often referred to as m-phenylenediamine) has been established for over a century. These diamines are typically synthesized via the reduction of the corresponding dinitrobenzene precursors and serve as fundamental monomers in the preparation of high-performance polymers, including aramids and epoxy hardeners, as well as in dyes and chemical intermediates. The addition of an alkoxy chain to the aromatic ring alters the solubility, thermal transitions, and assembly behavior of the resulting molecule in comparison with the parent diamine. This basic behaviour of long-chain substituted aromatic diamines underpins the utility of the 4-(dodecyloxy) derivative in materials research where both linear and amphiphilic characteristics are desired.([Benchchem][1]) Long chain alkoxy or alkyl substituents on aromatic diamines have been of interest in polymer and materials chemistry because they can disrupt tight chain packing and enhance solubility. Research on soluble polyimides bearing long chain alkyl side groups has shown that the incorporation of such substituents in diamine monomers leads to polymers with improved processability and distinct material properties such as lower glass transition temperatures and enhanced flexibility. Although these studies do not focus exclusively on 4-(dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine, they demonstrate the general principles and motivations for incorporating long alkoxy chains into aromatic diamines for advanced polymer applications.([Wiley Online Library][2]) The synthesis of 4-(dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine is generally achieved through multi-step organic transformations beginning with the introduction of the dodecyloxy group onto a suitably substituted aromatic precursor. A common strategy involves the Williamson ether synthesis between a hydroxybenzene derivative and a dodecyl halide under basic conditions to form the alkoxybenzene intermediate. Subsequent nitration of this intermediate, typically giving a dinitro compound, followed by catalytic hydrogenation, yields the desired diamine. Each step requires careful control of reaction conditions to avoid over-reaction or side products. The transformation of nitro groups to amino groups by catalytic hydrogenation (e.g., H2/Pd-C) is a well-established method for preparing aromatic amines.([Benchchem][1]) In materials applications, the two amino functionalities of 4-(dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine allow it to react as a monomer in step-growth polymerization reactions. When paired with diacid chlorides or dianhydrides, it can form polyamides or polyimides, respectively, through condensation reactions. The presence of the long dodecyloxy chain may increase the solubility of monomers and polymers in organic solvents, facilitating processing into films, coatings, or other macromolecular architectures. Such solubility enhancement is important when manufacturing advanced materials that require solution casting or spin coating techniques. Research into similar aromatic diamines with alkoxy substituents has shown that the resulting polymers can have tailored thermal and mechanical properties, which are advantageous for coatings, membranes, and optoelectronic materials.([Wiley Online Library][2]) Beyond polymer synthesis, the amphiphilic character of 4-(dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine suggests potential utility in self-assembly and supramolecular chemistry. Compounds combining hydrophobic alkyl segments with reactive aromatic cores are often explored in the formation of organized structures such as micelles or liquid crystalline phases. While specific peer-reviewed studies on the mesogenic behaviour of this exact compound are limited, analogous long-chain alkoxy substituted aromatics have been investigated in the context of liquid crystals and ordered assemblies. In summary, 4-(dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine is a specialized aromatic diamine derivative whose significance stems from combining a reactive phenylenediamine core with a long hydrophobic side chain. The compound is used as a monomer or intermediate in polymer science and materials chemistry, where its structural features can influence solubility and properties of derived materials. Its preparation and applications are consistent with broader trends in modifying aromatic diamines to tailor polymer behavior. References Nagase Y, Oku M, Iwasaki Y, Ishihara K (2007) Preparations of aromatic diamine monomers containing hydrophobic side chains and copolyamides: influence of side-chain structure on polymer properties. Polymer Journal 39 712–721 DOI: 10.1295/polymj.PJ2006253 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 4-(Dodecyloxy)benzene-1,3-diamine |