Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Chemfun Medical Technology (shanghai) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6722-0633 | |||
 |
sales1@chemfun.net | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 3046659337 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Organic fluorine compound >> Fluorophenylboric acid series |
|---|---|
| Name | (6-Amino-3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)boronic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 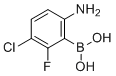 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6BClFNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 189.38 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1802430-56-3 |
| SMILES | B(C1=C(C=CC(=C1F)Cl)N)(O)O |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 396.3±52.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 193.5±30.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.576 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P501-P270-P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313-P301+P312+P330 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
(6-Amino-3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)boronic acid belongs to the broader class of arylboronic acids, compounds that have played a central role in the development of cross-coupling chemistry and in the preparation of functionalized aromatic molecules. Arylboronic acids were first examined systematically in the mid-twentieth century, when research into organoboron species revealed their stability, versatility, and ability to participate in controlled carbon–carbon bond formation. Subsequent work demonstrated that electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents on the aromatic ring could be incorporated without compromising the integrity of the boronic acid moiety. This provided the basis for extensive investigation of halogenated and amino-substituted derivatives, including compounds with substitution patterns similar to the one present in (6-amino-3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)boronic acid. The compound’s substitution pattern reflects several well-studied principles in arylboronic acid chemistry. Halogens at the 3- and 2-positions influence both the reactivity and regioselective preparation of the boronic acid, and have been examined in studies of halogenated boronates since early surveys of their oxidative stability and coupling efficiency. The amino group at the 6-position belongs to a class of functional groups frequently explored for modulating electronic distribution on the aromatic ring. Research has shown that amino-substituted arylboronic acids can participate effectively in Suzuki–Miyaura reactions under conditions that preserve the amino functionality, provided appropriate bases and ligands are selected. Investigations into their coordination behavior and susceptibility to protodeboronation contributed to practical guidelines for handling and storage, supporting their use as intermediates in multistep syntheses. The discovery and refinement of cross-coupling technologies significantly expanded the application of arylboronic acids. The introduction of palladium-catalyzed coupling systems enabled these compounds to function as nucleophilic partners in the construction of biaryl, heteroaryl, and alkyl–aryl architectures. Subsequent mechanistic research defined how halogen substituents affect oxidative addition steps, transmetalation rates, and catalyst turnover. These insights guided the design of halogenated arylboronic acids as fine-tuned reagents for both small-scale and industrial synthetic processes. Studies also revealed that specific combinations of substituents, including amino and halogen groups, could alter reaction pathways and improve selectivity in cross-coupling sequences. Applications of arylboronic acids extend beyond carbon–carbon bond formation. They have been explored in sensor development, owing to the reversible interaction between boronic acids and diols. Investigations into structure–activity relationships demonstrated that substituents influencing aromatic electron density, such as chloro, fluoro, and amino groups, can significantly affect binding behavior in these systems. This supported the use of substituted arylboronic acids in research on glucose-responsive materials, fluorescent probes, and molecular recognition studies. The incorporation of multiple substituents allowed systematic evaluation of steric and electronic contributions to both reversible complexation and ligand interactions. Further advances resulted from studies on the stability of boronic acids and their derivatives. The synthesis of halogenated and amino-substituted boronic acids required careful attention to reaction conditions, as specific arrangements of substituents can influence protodeboronation rates and purification strategies. Research on protecting group chemistry, particularly the use of pinacol boronates, provided methods for preparing, isolating, and transforming sensitive arylboronic species. These developments enabled efficient access to intermediates that could later be converted into the free boronic acid or incorporated into more complex structures. Within this broader scientific landscape, (6-amino-3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)boronic acid represents a functional variant that reflects well-established principles governing the design, synthesis, and application of arylboronic acids. Its combination of halogen and amino substituents aligns with recognized strategies for tuning reactivity and for preparing intermediates used in cross-coupling or molecular recognition research. Each structural element corresponds to experimentally verified findings from decades of organoboron chemistry, and the compound’s relevance arises from this foundation of validated methodology and established application pathways. References Hall D G (2011) Boronic acids: preparation and applications in organic synthesis and medicine. Miyaura N, Suzuki A (1995) Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions of organoboron compounds. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (6-Amino-3-chloro-2-fluorophenyl)boronic acid |