Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Great Forest Biomedical Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 2831-3180 | |||
 |
marketing@great-forest.com info@great-forest.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Extrasynthese Chemical S.A.S. | France | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+33 (47) 898-2034 | |||
 |
info@extrasynthese.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Wilshire Technologies, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (609) 683-1117 | |||
 |
Wilshire-info@evonik.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1997 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Aktin Chemicals Inc | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 400-028-7725 | |||
 |
info@aktinchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Chengdu Biopurify Phytochemicals Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (28) 8263-3860 8263-3987 | |||
 |
sales@biopurify.com biopurify@gmail.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Vegomega Biopharma Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18062552845 | |||
 |
vegomega@163.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2017 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Chinese herbal medicine ingredients |
|---|---|
| Name | Dihydrocapsaicin |
| Synonyms | 8-Methyl-N-vanillylnonanamide |
| Molecular Structure | 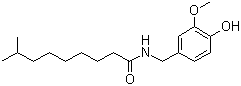 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H29NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 307.43 |
| CAS Registry Number | 19408-84-5 |
| EC Number | 606-308-7 |
| SMILES | CC(C)CCCCCCC(=O)NCC1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)OC |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.*Melting point|65.5-65.8 ºC |
|---|---|
| Index of Refraction | 1.510, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 497.4±35.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.* |
| Flash Point | 254.6±25.9 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H301-H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P273-P280-P301+P316-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P391-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3462 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dihydrocapsaicin is a pungent compound found in various Capsicum species, contributing significantly to the spiciness of chili peppers. It is a capsaicinoid, a group of compounds responsible for the heat associated with chili peppers. Dihydrocapsaicin was first isolated in the late 20th century during the extensive research on the chemical constituents of Capsicum species, which aimed to identify and characterize the compounds responsible for their unique flavor and pungency. The synthesis of dihydrocapsaicin can be achieved through various methods, including extraction from natural sources and chemical synthesis. Natural extraction typically involves the isolation of capsaicinoids from chili peppers using organic solvents, followed by purification processes such as chromatography. Alternatively, synthetic approaches have been developed to create dihydrocapsaicin in the laboratory, providing researchers with a reliable source of the compound for further studies. Dihydrocapsaicin has garnered significant interest for its various applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. In the food industry, it is primarily utilized as a flavoring agent and a natural preservative. Its ability to enhance flavor while providing a spicy kick makes it a popular ingredient in sauces, snacks, and seasoning blends. Additionally, dihydrocapsaicin is often used in spicy food products to provide consumers with a distinctive taste experience. In the pharmaceutical industry, dihydrocapsaicin has been studied for its potential therapeutic properties. Research has indicated that it possesses analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, making it a candidate for pain management formulations. Dihydrocapsaicin works by interacting with the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels, which are involved in pain sensation. This mechanism of action has led to the development of topical analgesic creams and patches containing dihydrocapsaicin to alleviate pain associated with conditions such as arthritis and neuropathic pain. Furthermore, dihydrocapsaicin has been explored for its potential health benefits beyond pain relief. Studies have suggested that it may have antioxidant properties, contributing to its role in promoting overall health. The compound has also been investigated for its potential effects on metabolism and weight management. Some research indicates that dihydrocapsaicin may enhance metabolic rate and fat oxidation, making it a subject of interest in the field of weight loss and obesity management. In the cosmetics industry, dihydrocapsaicin is being incorporated into products designed to improve skin health. Its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties make it a suitable ingredient for formulations targeting skin irritations and conditions such as rosacea. Additionally, its ability to enhance blood circulation may contribute to the effectiveness of certain cosmetic products, promoting healthier-looking skin. The versatility of dihydrocapsaicin has made it a valuable compound across various industries. As research continues, new applications and benefits are likely to be discovered, further expanding the potential uses of this fascinating capsaicinoid. Ongoing studies are also focused on understanding the optimal dosages and formulations that maximize the therapeutic effects of dihydrocapsaicin while minimizing any potential side effects. In summary, dihydrocapsaicin is a significant capsaicinoid with a rich history of discovery and diverse applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Its unique properties, coupled with its pungent flavor, make it a valuable ingredient in numerous products. As research advances, dihydrocapsaicin's potential benefits and applications will likely continue to evolve, solidifying its importance in various fields. References 2024. Relationship between Fruit Maturation, Phytochemical Content, Pungency, and Pun1 Gene Expression in Capsicum Species (Capsicum spp.). Russian Journal of Plant Physiology, 71(4). DOI: 10.1134/s1021443724607262 2024. Insights into the chili phytochemicals, bioactive components, and antioxidant activity of instant premixes (green and red chilies) and their reconstitution products. Food Production, Processing and Nutrition, 6(1). DOI: 10.1186/s43014-024-00248-2 2024. Novel derivatives of capsaicin as a potent hypolipidemic and anti-obesity agent. Molecular Diversity, 28(5). DOI: 10.1007/s11030-024-10971-0 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Dihydrocapsaicin |