Ethyl methyl carbonate is an organic carbonate ester with the molecular formula C4H8O3. Structurally, it consists of a central carbonate group (–O–C(=O)–O–) bonded to one ethyl and one methyl group. The combination of the carbonate functional group and two alkyl substituents imparts moderate polarity, chemical stability, and reactivity toward nucleophiles. Ethyl methyl carbonate is typically a colorless liquid with low viscosity, a mild ester-like odor, and solubility in common organic solvents, while having limited solubility in water.
The compound is primarily used as a solvent and intermediate in organic synthesis. Its carbonate functionality allows it to participate in transesterification, nucleophilic substitution, and esterification reactions. It is employed in the synthesis of other carbonates, carbamates, and as a mild alkylating agent for organic transformations.
Ethyl methyl carbonate also finds application in the formulation of electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Its moderate dielectric constant, low viscosity, and chemical stability make it suitable for dissolving lithium salts and facilitating ion transport. In such applications, it is often combined with other carbonate solvents to optimize electrolyte performance, including conductivity, electrochemical stability, and low-temperature operation.
The compound can be synthesized by the transesterification of dimethyl carbonate with ethanol or by the reaction of methyl chloroformate with ethanol under controlled conditions. These methods provide efficient production routes with minimal byproducts and good selectivity for the desired ethyl methyl carbonate. Handling precautions include avoiding contact with strong oxidizers and open flames, as it is flammable and can react under aggressive chemical conditions.
Overall, ethyl methyl carbonate is a versatile carbonate ester used as a solvent, chemical intermediate, and electrolyte component. Its combination of a reactive carbonate group and small alkyl substituents provides both reactivity and solubility, making it valuable in organic synthesis, battery technology, and other industrial applications.
References
2025. Preparation and electrochemical performance of LiF-V2O3 composite cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics.
DOI: 10.1007/s11581-025-06542-4
2025. Conductive NaTi2(PO4)3/C nanocomposite by spray drying for enhanced sodium energy storage. Ionics.
DOI: 10.1007/s11581-025-06541-5
|

















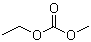
 GHS02 DangerGHS02 Details
GHS02 DangerGHS02 Details