Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Changsha Hecom Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (731) 8578-1688 | |||
 |
tan@emdchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Rech Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (731) 8586-4603 | |||
 |
business@rqsulfates.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1991 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Medilink Pharmachem | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (79) 3007-0133 | |||
 |
exports@medilinkpharma.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 1996 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Labseeker Inc | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (858) 750-1632 | |||
 |
marketing@labseeker.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (852) 3060-6658 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Vitamins and minerals >> Trace elements and mineral drugs |
|---|---|
| Name | Zinc sulphate |
| Molecular Structure | 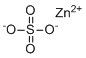 |
| Molecular Formula | ZnSO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 161.45 |
| CAS Registry Number | 7733-02-0 |
| EC Number | 231-793-3 |
| SMILES | [O-]S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Zn+2] |
| Solubility | Soluble (water) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.97 g/mL g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 100 ºC |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS05;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H318-H400-H410 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Safety Description | S26;S39;S61 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3082;UN 9161 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The discovery of zinc sulphate dates back centuries, tracing its origins to the recognition of the medicinal properties of zinc and sulphur compounds. Zinc, an essential mineral, plays a pivotal role in numerous physiological processes, including immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. Sulphate, derived from sulfur, is known for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties. The combination of these two elements in the form of zinc sulphate represents a potent therapeutic agent with diverse applications in medicine. Initially utilized in traditional medicine for its wound-healing properties, zinc sulphate gained prominence as a treatment for various dermatological conditions, including acne, eczema, and diaper rash. In recent years, zinc sulphate has garnered attention for its role in the management of common cold symptoms. Zinc sulphate exerts its antiviral effects by inhibiting viral replication and modulating immune responses, making it a valuable adjunct therapy for respiratory infections. Moreover, zinc sulphate holds promise in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, such as diarrhea and peptic ulcers. As an essential nutrient for intestinal epithelial integrity, zinc plays a crucial role in maintaining gut barrier function and mucosal immunity. Beyond its topical and oral applications, zinc sulphate has found utility in ophthalmology as a treatment for eye conditions like conjunctivitis and blepharitis. Its antimicrobial properties help combat bacterial and viral infections, while its anti-inflammatory effects reduce ocular inflammation and discomfort. In veterinary medicine, zinc sulphate is used in the treatment of hoof disorders in livestock, such as foot rot in cattle and thrush in horses. Its antiseptic properties aid in disinfecting wounds and promoting tissue regeneration, facilitating the healing process in animals. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Zinc sulphate |