Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Haimen RuiYi Medical Tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5471-1706 | |||
 |
sales@ruiyitech.com zyj3625@msn.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Forsman Scientific (beijing) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 8483-3890 | |||
 |
info@forsman.com.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2013 | ||||
| Fluoropharm Co.,Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-6753 +86 13336034509 | |||
 |
sales@fluoropharm.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2013 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Hangzhou Molcore Biopharmatech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8102-5280 | |||
 |
sales@molcore.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Lavin Chemical (nantong) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13862887077 | |||
 |
lavin@lavinchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Fatty alcohol |
|---|---|
| Name | 1-Ethynyl-1-cyclohexanol |
| Synonyms | 1-Ethynylcyclohexanol |
| Molecular Structure | 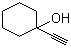 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H12O |
| Molecular Weight | 124.18 |
| CAS Registry Number | 78-27-3 |
| EC Number | 201-100-9 |
| SMILES | C#CC1(CCCCC1)O |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.967 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 30 - 33 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 174.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 180 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 62.8 ºC (Calc.)*, 73 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: 10 g/L (20 ºC) (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.494 (Calc.)*, 1.483 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H311-H315-H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P262-P264-P264+P265-P270-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P316-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P361+P364-P362+P364-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2811 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1-Ethynyl-1-cyclohexanol is an alkynyl alcohol with the molecular formula C8H12O. Structurally, it consists of a cyclohexane ring substituted at the 1-position with both a hydroxyl group (–OH) and an ethynyl group (–C≡CH), giving a tertiary alcohol bearing a terminal alkyne. The combination of a polar hydroxyl group and a reactive terminal alkyne confers both hydrogen-bonding capability and nucleophilic character at the alkyne carbon. The compound is typically a colorless to pale yellow liquid, soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and dichloromethane, but with limited solubility in water. 1-Ethynyl-1-cyclohexanol is primarily used as a building block in organic synthesis. The terminal alkyne allows for a wide range of reactions, including nucleophilic additions, Sonogashira couplings, and click chemistry, enabling the preparation of more complex molecules such as substituted cyclohexanes, heterocycles, and functionalized alcohols. The hydroxyl group provides an additional site for esterification, etherification, or oxidation reactions, making it versatile for multi-step synthetic routes. The compound is also employed in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates and specialty chemicals, where the combination of cyclic structure, alkyne functionality, and tertiary alcohol provides a scaffold for introducing functional diversity. Its reactivity and steric properties are particularly useful in stereoselective and regioselective transformations. Synthetically, 1-ethynyl-1-cyclohexanol can be prepared by the addition of acetylene to cyclohexanone under basic or catalytic conditions, forming the tertiary alcohol with the ethynyl substituent at the 1-position. Handling precautions include avoiding exposure to open flames or strong oxidizing agents, as terminal alkynes are flammable and potentially reactive under certain conditions. Overall, 1-ethynyl-1-cyclohexanol is a versatile alkynyl alcohol with dual functional groups—a terminal alkyne and a tertiary hydroxyl—attached to a cyclohexane ring. Its structural features and reactivity make it a valuable intermediate in organic synthesis, pharmaceutical development, and the preparation of functionalized cyclic compounds. References 2023. An insight on medicinal attributes of 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-triazole derivatives as alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors. Molecular Diversity. DOI: 10.1007/s11030-023-10728-1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1-Ethynyl-1-cyclohexanol |