Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Chemtrade International Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (532) 8689-3005 | |||
 |
chemtrade@trade-chem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Shandong Baolingbao Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (534) 212-6099 891-8699 212-6077 | |||
 |
baolingbao@blb-cn.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Gremount International Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 5969-3741 5969-3742 5969-3743 | |||
 |
logistics@gremount.com.cn | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Sanxinyuan Food Industry Corp.Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (534) 7126-6078 | |||
 |
export@sanxinyuanfood.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1997 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Carbohydrate >> Polysaccharide |
|---|---|
| Name | Maltodextrin |
| Synonyms | MLD |
| Molecular Structure | 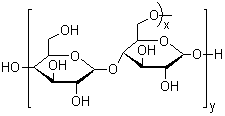 |
| CAS Registry Number | 9050-36-6 |
| EC Number | 232-940-4 |
| SMILES | O[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O)[C@H](O)CO |
| Melting point | 240 ºC (dec.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide commonly used as a food additive and functional ingredient in pharmaceuticals and industrial formulations. It is produced by the partial hydrolysis of starch, typically from corn, wheat, rice, or potato. The process involves the enzymatic or acid-catalyzed breakdown of starch into smaller glucose polymers, resulting in a white, hygroscopic powder that is soluble in water and has a mildly sweet to neutral taste depending on the degree of hydrolysis. The discovery and commercial development of maltodextrin is closely linked to advances in carbohydrate chemistry and food processing technologies during the 20th century. As enzymatic hydrolysis methods became more efficient and cost-effective, it became feasible to produce maltodextrin at industrial scale. Its production is standardized by the dextrose equivalent (DE), which indicates the degree of hydrolysis and correlates with its sweetness and reducing sugar content. Maltodextrins typically have a DE value less than 20, distinguishing them from glucose syrups. In the food industry, maltodextrin serves multiple purposes. It is widely used as a bulking agent, texturizer, stabilizer, and carrier for flavorings and colors. Due to its neutral flavor and high solubility, it can be blended easily with other ingredients, contributing to mouthfeel and improving the consistency of powdered and processed products. Common food applications include powdered drink mixes, instant soups, sauces, dairy products, confectionery, and nutritional supplements. Maltodextrin also plays an important role in the formulation of low-fat and reduced-calorie foods. It can mimic the texture and mouthfeel of fats without contributing significant fat content, thereby enabling manufacturers to meet consumer demand for lighter food options. Additionally, it is used as an encapsulating agent for spray-drying volatile compounds such as flavor oils, vitamins, and probiotics, helping to protect them from oxidation and moisture while improving shelf life. In sports and clinical nutrition, maltodextrin is valued for its rapid digestibility and high glycemic index. It is commonly included in carbohydrate-rich supplements intended for athletes or patients requiring fast energy delivery. Upon ingestion, it is quickly broken down into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream, making it suitable for use in energy drinks, recovery formulas, and parenteral nutrition. Outside the food and nutritional sectors, maltodextrin finds application in pharmaceutical and industrial products. In pharmaceuticals, it is used as a filler and binder in tablet and capsule formulations, as well as a carrier for active ingredients in powdered medications. Its compatibility with other excipients and its generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status make it an attractive excipient for oral and topical dosage forms. In cosmetics and personal care products, maltodextrin is used as a viscosity-regulating agent, film former, and moisture-retaining additive. It can be found in formulations such as creams, lotions, and hair care products, where it contributes to product stability and sensory attributes. Maltodextrin's widespread use has prompted extensive evaluation of its safety and regulatory status. It is considered non-toxic and safe for consumption by major food safety authorities, including the United States Food and Drug Administration and the European Food Safety Authority. Although derived from starch sources that may include wheat, manufacturing processes can reduce gluten content to levels considered acceptable for gluten-free labeling, depending on local regulations. However, individuals with specific health conditions such as diabetes may need to monitor maltodextrin intake due to its high glycemic impact. In rare cases, maltodextrin can cause allergic reactions or gastrointestinal discomfort, particularly when consumed in large quantities. In conclusion, maltodextrin is a versatile and widely used polysaccharide derived from starch, valued for its functional properties across food, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications. Its role as a carrier, texturizer, and carbohydrate source has made it a staple ingredient in many consumer products, supported by decades of safe use and regulatory approval. References 2007. Contribution of mucosal maltase-glucoamylase activities to mouse small |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Maltodextrin |