Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Tianjin Zhongxin Chem-tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (22) 6688-0623 | |||
 |
sales@tjzxchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Jiangsu Evergreen New Material Technology Incorporated | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (025) 8491-1160 | |||
 |
flora.wang@cqsgfz.cn | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13605178468 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +8613605178468 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Scientific Polymer Products, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (585) 265-0413 | |||
 |
custserv@scipoly.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Anvia Chemicals, LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (414) 534-7845 | |||
 |
sales@anviachem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Changsha Chromar Pharmaceutical Techno. Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (731) 8469-7086 | |||
 |
1249217438@qq.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| Crescent Chemical Co. Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 348-0333 | |||
 |
crescent@creschem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Hydrocarbon compounds and their derivatives >> Aromatic hydrocarbon |
|---|---|
| Name | 2-Phenyl-1-propene |
| Synonyms | alpha-Methylstyrene; Isopropenylbenzene |
| Molecular Structure | 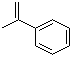 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H10 |
| Molecular Weight | 118.18 |
| CAS Registry Number | 98-83-9 |
| EC Number | 202-705-0 |
| SMILES | CC(=C)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Density | 0.909 |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -23 ºC |
| Boiling point | 165-169 ºC |
| Refractive index | 1.537-1.539 |
| Flash point | 45 ºC |
| Water solubility | insoluble |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS02;GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS02;GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H226-H335-H319-H411 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264+P265-P271-P273-P280-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P337+P317-P391-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2303 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2-Phenyl-1-propene, also known as allylbenzene, is an organic compound characterized by its phenyl group attached to a propene chain. The compound's structure consists of a three-carbon propene backbone with a phenyl substituent at the second carbon, giving it distinct chemical properties. The discovery of 2-phenyl-1-propene can be traced back to the early explorations of alkenes and aromatic compounds in organic chemistry during the 19th century, as chemists began to understand the significance of substitution patterns in hydrocarbon structures. 2-Phenyl-1-propene is predominantly synthesized through the dehydrogenation of phenylpropane or by the elimination of hydrogen chloride from phenyl-2-propyl chloride. This synthetic approach allows for the selective formation of the desired alkene while minimizing byproducts, making it an efficient method for producing this compound in laboratory and industrial settings. The applications of 2-phenyl-1-propene are diverse, particularly in the field of organic synthesis and as a chemical intermediate. It serves as a precursor in the synthesis of various important chemicals, including pharmaceuticals and fragrances. Its structure makes it suitable for a range of reactions, such as electrophilic addition, Diels-Alder reactions, and polymerization, facilitating the creation of more complex molecular architectures. In the fragrance industry, 2-phenyl-1-propene is valued for its pleasant floral scent, often described as reminiscent of jasmine or other floral notes. It is incorporated into perfumes and scented products to enhance their aromatic profile. The compound's volatility and compatibility with other fragrance ingredients make it a popular choice for formulators looking to create sophisticated and appealing scents. Additionally, 2-phenyl-1-propene finds applications in the production of polymers and resins. It can be used as a monomer in polymerization reactions to produce various copolymers with desirable properties. These polymers are utilized in applications ranging from coatings and adhesives to specialty plastics, highlighting the compound's versatility in materials science. While 2-phenyl-1-propene has significant industrial applications, safety considerations are paramount. As with many organic compounds, it is essential to handle this substance with care, adhering to safety guidelines to minimize risks associated with exposure. The compound is generally considered safe when used appropriately, but regulatory assessments ensure that manufacturers follow established standards to protect consumer health and safety. Recent research continues to explore the potential of 2-phenyl-1-propene in novel applications, including its role in the development of new materials and as a building block for innovative chemical syntheses. As scientists investigate its properties further, 2-phenyl-1-propene may find additional uses that enhance its significance in both existing and emerging fields. In summary, 2-phenyl-1-propene is an important organic compound with diverse applications in organic synthesis, fragrances, and materials science. Its unique structure and chemical properties enable it to serve as a valuable intermediate and additive in various formulations. Continued research may reveal even more applications for this versatile compound. References 2024. A Comprehensive Exploration of the Synergistic Relationship between DMSO and Peroxide in Organic Synthesis. Topics in Current Chemistry (Cham), 72(11). DOI: 10.1007/s41061-024-00482-9 2024. Efficient and selective oxidation of alcohols and hydrocarbons catalyzed by oxovanadium(IV) unsymmetrical salophen complex supported on silica-coated CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 46(11). DOI: 10.1007/s13738-024-03128-1 2024. Schiff Base-Based Molybdenum Complexes as Green Catalyst in the Epoxidation Reaction: A Minireview. Topics in Current Chemistry (Cham), 72(10). DOI: 10.1007/s41061-024-00480-x |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2-Phenyl-1-propene |