Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Qingdao Free Trade Zone United International Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (532) 83893696 +86 13808950921 | |||
 |
jason.wang@unitedint.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Shanghai Cloudscape Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6630-2580 | |||
 |
mollyqin@cschemsh.com molly0919@hotmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2016 | ||||
| Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. | Japan | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+81 (6) 6203-3741 | |||
 |
wkhk.info@fujifilm.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1922 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyridine compound >> Ethylpyridine |
|---|---|
| Name | 2-Ethylpyridine |
| Molecular Structure | 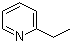 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9N |
| Molecular Weight | 107.15 |
| CAS Registry Number | 100-71-0 |
| EC Number | 202-881-9 |
| SMILES | CCC1=CC=CC=N1 |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.937 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -63 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 150.3±3.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 149 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 29.4 ºC (Calc.)*, 37 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: ~45 g/L (20 ºC) (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.499 (Calc.)*, 1.496 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS02;GHS07 WarningGHS02; Details
GHS02;GHS07 WarningGHS02; Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H226-H312+H332-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P403+P233-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 1993 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2-Ethylpyridine is a substituted pyridine in which an ethyl group occupies the position adjacent to the ring nitrogen. It belongs to the broader family of alkylpyridines, a class of heteroaromatic compounds that have been studied extensively because of their occurrence in coal tar, their characteristic basicity, and their usefulness as intermediates in chemical synthesis. The compound is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a strong, penetrating odor, reflecting the typical sensory properties of low-molecular-weight pyridine derivatives. The discovery of 2-ethylpyridine is closely connected to the historical investigation of coal tar in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. During this period, chemists systematically separated and characterized nitrogen-containing bases obtained from coal tar distillation. Pyridine itself was identified first, followed by a variety of alkyl-substituted pyridines, including the ethylpyridines. Early studies established that 2-ethylpyridine could be isolated as a minor component of coal tar bases and distinguished from its positional isomers by differences in boiling point, salt formation, and reactivity. These investigations played an important role in understanding how alkyl substitution affects the electronic properties and steric environment of the pyridine ring. As synthetic organic chemistry advanced, laboratory methods for preparing 2-ethylpyridine were developed, allowing the compound to be obtained in higher purity and larger quantities than was possible from coal tar isolation alone. Synthetic routes generally relied on ring-forming reactions or alkylation strategies starting from simpler nitrogen-containing precursors. Through such work, chemists confirmed the structure of 2-ethylpyridine and clarified how substitution at the 2-position influences basicity and coordination behavior compared with unsubstituted pyridine and other alkylpyridine isomers. These foundational studies established 2-ethylpyridine as a well-defined and reproducible chemical substance suitable for further application. In terms of application, 2-ethylpyridine has been used primarily as an intermediate in organic synthesis. Its heteroaromatic ring and basic nitrogen atom make it a useful building block for the preparation of more complex molecules. In particular, it has served as a precursor in the synthesis of agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals, where the pyridine motif is valued for its ability to modulate biological activity and physicochemical properties. Substitution at the 2-position can introduce steric effects that influence binding interactions in biologically active compounds, making 2-ethylpyridine-derived structures attractive in medicinal chemistry research. Another important area of application is coordination and catalytic chemistry. Like pyridine, 2-ethylpyridine can act as a ligand toward transition metals, donating its lone pair of electrons on nitrogen to form coordination complexes. The presence of the ethyl substituent alters both the steric profile and the electron-donating properties of the ligand, which can affect metal–ligand bond strength and catalytic performance. As a result, 2-ethylpyridine and related alkylpyridines have been examined as modifiers or auxiliary ligands in homogeneous catalysis and organometallic chemistry. 2-Ethylpyridine has also found use as a solvent or additive in specific industrial and laboratory contexts. Its moderate basicity allows it to neutralize acidic byproducts or stabilize reactive intermediates in certain reactions. Additionally, alkylpyridines, including 2-ethylpyridine, have been studied for their roles in flavors and odors, particularly as contributors to roasted or smoky aromas, although such applications are generally indirect and rely on controlled formulation rather than the pure compound itself. Overall, the history of 2-ethylpyridine reflects the broader development of heterocyclic chemistry, from early isolation from complex natural mixtures to deliberate synthesis and targeted application. Its continued use as a chemical intermediate and ligand underscores the enduring importance of simple substituted pyridines in both fundamental research and applied chemical industries. References Furst AF (1949) The reduction of 2-acetylpyridine to 2-ethylpyridine. Journal of the American Chemical Society 71(10) 3550–3551 DOI: 10.1021/ja01178a513 Malik M, Świtlicka A, Bieńko A, Komarnicka UK, Bieńko DC, Kozieł S, Kyzioł A, Mazur T, Machura B (2022) Copper(ii) complexes with 2-ethylpyridine and related hydroxyl pyridine derivatives: structural, spectroscopic, magnetic and anticancer in vitro studies. RSC Advances 12 27648–27665 DOI: 10.1039/D2RA05133H Morais VMF, Miranda MS, Matos MAG (2003) Thermochemical study of the ethylpyridine and ethylpyrazine isomers. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry (Issue 23) — DOI available on publisher site but search by title on RSC Publishing. DOI: 10.1039/B308097H |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2-Ethylpyridine |