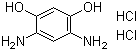
4,6-Diaminoresorcinol dihydrochloride is an aromatic diamine salt with the molecular formula C6H8Cl2N2O. Structurally, it consists of a resorcinol (1,3-dihydroxybenzene) core in which the hydroxyl groups at the 1 and 3 positions remain intact, and the 4 and 6 positions are substituted with amino groups. The dihydrochloride form results from protonation of the amino groups with hydrochloric acid, yielding a water-soluble salt. This compound typically appears as a crystalline solid with good solubility in water and polar organic solvents, but limited solubility in nonpolar media.
The presence of amino groups at the 4 and 6 positions makes this compound highly reactive toward electrophiles. It can participate in condensation reactions with aldehydes, ketones, or acid derivatives, enabling its use as a building block in the synthesis of dyes, polymers, and heterocyclic compounds. The resorcinol core contributes to hydrogen bonding and stabilization of resulting products, while the dihydrochloride form enhances solubility and handling in aqueous systems.
In organic synthesis, 4,6-diaminoresorcinol dihydrochloride is particularly valuable for preparing azo and heterocyclic dyes, as the amino groups can be diazotized and coupled to other aromatic compounds to form colored conjugated structures. It is also used in polymer chemistry for generating crosslinked networks, where the amino groups react with suitable electrophilic linkers to produce functional materials with defined optical or chemical properties.
The compound can be synthesized by selective amination of resorcinol derivatives followed by treatment with hydrochloric acid to generate the dihydrochloride salt. Its handling requires standard laboratory precautions for aromatic amines and acid salts, including the use of gloves and eye protection.
Overall, 4,6-diaminoresorcinol dihydrochloride is a water-soluble aromatic diamine salt with high reactivity and versatility. Its combination of a resorcinol core, two amino substituents, and enhanced solubility through dihydrochloride formation makes it a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of dyes, polymers, and heterocyclic compounds, with applications in both chemical research and industrial chemistry.
References
2022. Preparation of High-performance Polyimide Fibers with Wholly Rigid Structures Containing Benzobisoxazole Moieties. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 40(4).
DOI: 10.1007/s10118-022-2666-8
2018. Polyimides Containing Benzoxazole Units and Their Liquid-Crystalline Behavior. Macromolecular Research, 26(9).
DOI: 10.1007/s13233-018-6125-x
|



















 GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details