Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Jinxiang Chemical (Danyang) Products Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8681-9862 +86 13913839793 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com nancy-zong@hotmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| SLN Pharmachem | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (22) 2870-1926 6524-0421 2854-9125 | |||
 |
ho@slnpharmachem.com office@slnpharmachem.co.in | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1997 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Jubilant Organosys Ltd. | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (120) 436-1221 | |||
 |
puneet_malik@jubl.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Ring Specialty Chemicals Inc. | Canada | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (416) 493-6870 | |||
 |
info@ringchemicals.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Nanjing Tengxiang Imp&Exp Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8681-9862 +86 13913839793 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2018 | ||||
| Shanghai Tajilin Industrial Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5063-0626 | |||
 |
sales003@tajilin.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2019 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2020 | ||||
| Nanjing Shunxiang Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (025) 8681-9868 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyridine compound >> Pyridine derivative |
|---|---|
| Name | Pyridine hydrobromide |
| Molecular Structure | 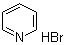 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N.HBr;C5H6BrN |
| Molecular Weight | 160.01 |
| CAS Registry Number | 18820-82-1 |
| EC Number | 242-600-7 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=NC=C1.Br |
| Melting point | 200 ºC (Decomposes) (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pyridine hydrobromide is the hydrobromide salt of pyridine formed through protonation of the aromatic nitrogen atom by hydrobromic acid. The reaction produces the pyridinium cation paired with a bromide anion, yielding a stable ionic compound that typically occurs as a white to off-white hygroscopic crystalline solid. The material is readily soluble in water and other polar solvents, and its preparation represents one of the fundamental examples of acid–base behavior in heteroaromatic chemistry. The salt has been known since early investigations into pyridine and its derivatives, when the behavior of pyridinium ions was explored to understand reactivity patterns and the influence of protonation on aromatic nitrogen heterocycles. The historical study of pyridinium salts developed alongside research into coal-tar–derived heterocycles during the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Pyridine itself was first isolated from bone oil and later from coal tar, and as its chemical behavior became better understood, the formation of pyridinium halides emerged as an important method for modifying reactivity. Pyridine hydrobromide was naturally investigated because hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids available for generating a stable pyridinium salt. These early investigations established the salt as a convenient and isolable form of protonated pyridine, allowing researchers to study protonation equilibria, salt formation, and transformations mediated by pyridinium species. Pyridine hydrobromide is closely associated with the chemistry of brominating agents derived from pyridinium salts. One of the most historically significant developments in this area was the use of pyridinium hydrobromide perbromide, prepared by treating pyridine hydrobromide with bromine. This reagent became a standard tool for electrophilic bromination of organic substrates and played an important role in the advancement of synthetic organic chemistry in the mid-twentieth century. The parent salt, pyridine hydrobromide, is integral to this chemistry because its controlled protonation state and reactivity allow it to serve as a precursor for brominating reagents and as a source of bromide under defined conditions. In laboratory synthesis, pyridine hydrobromide has been employed in reactions requiring mild acidity combined with the presence of bromide ions. It supports certain halogenation reactions, particularly those involving activated carbonyl compounds, where the pyridinium ion can modulate the acidity of the medium while bromide acts as a nucleophile or participates in electrophilic transformations when oxidized. These properties make the salt useful in transformations that require a balance between protonation and nucleophilic or electrophilic bromine availability. Another established application lies in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates. Pyridine hydrobromide has been described as a reagent or catalyst in processes used to prepare intermediates for β-lactam antibiotics, including cephalosporin derivatives. In these roles, the compound contributes controlled acidic conditions necessary for selective transformations involving heterocyclic substrates. The pyridinium ion can assist in activating functional groups or stabilizing intermediates, while the bromide counterion influences reaction pathways under strongly acidic media. Industrial synthetic processes also make use of pyridine hydrobromide as a starting material or intermediate in the preparation of brominating reagents that are safer or easier to handle than elemental bromine. Through its conversion into pyridinium hydrobromide perbromide or related species, it supports bromination steps in the manufacture of dyes, agrochemical intermediates, and specialty chemicals. Its solid form and relative stability are advantageous in settings where precise metering of reagents is required. In academic research, pyridine hydrobromide continues to be used as a reference compound for understanding the effects of protonation on heteroaromatic reactivity. The pyridinium ion influences aromatic substitution patterns, acid–base equilibria, and reaction mechanisms involving nitrogen-containing heterocycles. These properties make the hydrobromide salt valuable in mechanistic studies and in teaching contexts where model systems are needed to illustrate fundamental organic chemistry principles. Overall, pyridine hydrobromide represents a long-established and well-characterized pyridinium salt with recognized importance in both laboratory and industrial chemistry. Its formation by simple acid–base reaction, combined with its roles in bromination chemistry, pharmaceutical intermediate preparation, and mechanistic studies of heterocycles, has ensured its continuing relevance in organic synthesis. References Djerassi C (1948) Brominations with pyridinium hydrobromide perbromide. Journal of the American Chemical Society 70 509–514 DOI: 10.1021/ja01181a508 Yang S-H (2009) Pyridinium hydrobromide perbromide: a versatile reagent in organic synthesis. Synlett 2009(08) 1351–1352 DOI: 10.1055/s-0029-1216645 Islam M B, Khan S (2023) Recent advances in pyridine scaffold: focus on chemistry of derivatives. Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 60 987–1001 DOI: 10.1155/2023/9967591 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Pyridine hydrobromide |