Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Jinxiang Chemical (Danyang) Products Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8681-9862 +86 13913839793 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com nancy-zong@hotmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Kingfirst Chemical (Nanjing) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8452-2992 8477-3604 | |||
 |
marketing@kingfirstchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Jubilant Organosys Ltd. | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (120) 436-1221 | |||
 |
puneet_malik@jubl.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| DanYang HengAn Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (511) 8663-9366 | |||
 |
info@hachem.cn suqianxff@hotmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1998 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Jinan Fufang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (531) 6659-3191 | |||
 |
fufangchem@126.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyridine compound >> Pyridine derivative |
|---|---|
| Name | Pyridine hydrochloride |
| Synonyms | Pyridinium chloride |
| Molecular Structure | 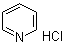 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H5N.HCl;C5H6ClN |
| Molecular Weight | 115.56 |
| CAS Registry Number | 628-13-7 |
| EC Number | 211-027-4 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=NC=C1.Cl |
| Melting point | 145 - 147 ºC (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 222 - 224 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: 85 g/100 mL (Expl.) |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302+H332-H302-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pyridine hydrochloride, also known as pyridinium chloride, is the crystalline salt formed by protonation of pyridine with hydrochloric acid, yielding the C5H5NH+ cation paired with a chloride anion. It typically appears as white to off-white hygroscopic crystals that melt around 144-147 °C and decompose on boiling, with good solubility in water and common polar organic solvents. The pKa of the pyridinium ion is approximately 5, reflecting its acidity relative to typical ammonium species and illustrating how protonation affects the basicity and reactivity of heteroaromatic nitrogen. Its simple preparation by passing hydrogen chloride into pyridine enables isolation of a stable salt widely used in laboratory and industrial settings. The origins of pyridine hydrochloride trace back to the early development of heterocyclic chemistry, in which pyridine itself was obtained from coal tar and studied for its basic and aromatic properties. Protonated pyridinium salts such as the hydrochloride arose naturally from explorations of acid–base chemistry involving heteroaromatic systems and were soon adopted as reagents and intermediates. The straightforward formation of the salt by the reaction of pyridine with hydrochloric acid exemplifies basic acid–base behavior, and its structural characterization revealed how protonation affects ring electronics and intermolecular interactions. In synthetic organic chemistry, pyridine hydrochloride serves as a reagent and intermediate in a diverse range of transformations. Its Brønsted acidic character and the presence of the pyridinium ion make it useful for promoting substitution reactions, ether cleavage, and the synthesis of chloro and hydroxy derivatives in pyridine and quinoline series under conditions where conventional reagents might be less selective. Researchers have demonstrated its effectiveness in converting bromo derivatives to chloro hydroxy compounds via electrophilic substitution pathways, enabling access to functionalized heterocycles that are important in medicinal and materials chemistry. Beyond acting as a reagent, pyridine hydrochloride is also used as a protic ionic medium in which polar reactants can be solubilized and activated. In some methodologies, it is employed to provide controlled acidic conditions that facilitate dehydration, N-demethylation, or cyclodehydration reactions without introducing strong mineral acids that might lead to competing side reactions. Its behavior as a hydrogen-bond donor and proton source has been exploited in transformations requiring mild protonation of substrates or activation of leaving groups. Pyridine hydrochloride also finds application in the preparation of other pyridinium salts and heterocyclic derivatives. Quaternization reactions of pyridine with various electrophiles yield pyridinium species that are key intermediates for catalysts, ionic liquids, phase transfer reagents, and bioactive scaffolds. In these processes, the chloride counter-ion from pyridine hydrochloride may be retained or exchanged to tune solubility and reactivity, making the salt a useful building block in the synthesis of functional materials. Physically, the salt’s hygroscopic nature and propensity to absorb moisture necessitate storage under dry conditions to preserve its integrity. Its stability as a crystalline material facilitates handling in the solid state and enables accurate dosing in organic reactions. Safety considerations include its irritancy and potential hazards upon contact with skin or inhalation, requiring standard protective measures in the laboratory. Overall, pyridine hydrochloride is a fundamental pyridinium salt whose ease of preparation, stable ionic structure, and utility as both reagent and intermediate have made it a mainstay in synthetic organic chemistry. Its applications in facilitating functional group transformations, promoting selective substitution reactions, and serving as a building block for more elaborate pyridinium derivatives underscore its enduring relevance in research and industrial processes. References Mongin F, Mongin O (1996) Pyridine hydrochloride: a new reagent for the synthesis of o-chloro hydroxy derivatives in pyridine and quinoline series. Tetrahedron Letters 37(37) 6695–6698 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(96)01449-9 Sowmiah S, Esperança JMS, Rebelo LPN, Afonso CAM (2018) Pyridinium salts: from synthesis to reactivity and applications. Organic Chemistry Frontiers 5(5) 453–493 DOI: 10.1039/C7QO00836H Wilson MW (2001) Pyridinium chloride. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. Wiley DOI: 10.1002/047084289X.rp287m |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Pyridine hydrochloride |