Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Jinxiang Chemical (Danyang) Products Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8681-9862 +86 13913839793 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com nancy-zong@hotmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Nanjing Dirise Chemcial Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 5216-1033 +86 15312098939 | |||
 |
sales@njdrschem.com piaobodechuan1978@hotmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Beijing Huikang Boyuan Chemical Tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 6886-2197 6886-7502 | |||
 |
market@huikangchem.com sales@huikangchem.com sales3@huikangchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2005 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Zhangjiagang Xikai Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5570-1600 | |||
 |
xikaiindustry@gmail.com sales@xikaichem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| SL Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (40) 6661-1133 | |||
 |
enquiry@sldrugs.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 1999 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| KS Laboratories Co., Ltd. | South Korea | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+82 (61) 753-9717 | |||
 |
semiyong@kslabo.co.kr | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Zhangjiagang Clent Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5881-3106 +86 13962460297 | |||
 |
sales@clentchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Ester >> Ethyl ester compound |
|---|---|
| Name | Diethyl azodicarboxylate |
| Synonyms | Azodicarboxylic acid diethyl ester; DEAD |
| Molecular Structure | 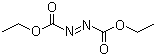 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H10N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 174.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1972-28-7 |
| EC Number | 217-821-7 |
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)/N=N/C(=O)OCC |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.106 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 226.3 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 250.7 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 106.9±13.2 ºC (Calc.)*, 85 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.472 (Calc.)*, 1.421 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS01;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS01;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H240-H302-H312-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P234-P235-P240-P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P317-P319-P321-P330-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P372+P380+P373-P403-P403+P233-P405-P410-P411-P420-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3233 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Diethyl azodicarboxylate is an azo compound with the molecular formula C6H10N2O4 that has played a central role in the development of modern synthetic organic chemistry. It is commonly abbreviated as DEAD and is recognized as a highly reactive electrophilic reagent. The compound appears as a red to orange liquid and is sensitive to heat, light, and reducing agents. Its defining structural feature is the azo functional group flanked by two electron-withdrawing carbamate ester groups, which strongly influence its reactivity and chemical behavior. The compound was first prepared and characterized in the mid-twentieth century during systematic studies of azo compounds and their redox properties. Early investigations focused on its synthesis from hydrazine derivatives and dialkyl carbonates, which allowed chemists to access a class of azo esters with controlled substitution patterns. These studies established diethyl azodicarboxylate as a stable yet highly activated azo compound, suitable for use as a reagent rather than merely a subject of structural interest. Its distinct color and redox activity also made it useful for mechanistic investigations into electron transfer and nucleophile–electrophile interactions. The most significant milestone in the history of diethyl azodicarboxylate was its incorporation into what became known as the Mitsunobu reaction. This transformation, developed in the 1960s, demonstrated that diethyl azodicarboxylate could be combined with triphenylphosphine and an alcohol to enable substitution reactions under mild conditions. The reaction allowed alcohols to be converted into a wide range of functional groups, including esters, ethers, thioethers, and nitrogen-containing derivatives, often with inversion of configuration at a stereogenic center. This application firmly established diethyl azodicarboxylate as a cornerstone reagent in stereoselective synthesis. Beyond its role in the Mitsunobu reaction, diethyl azodicarboxylate has been used as an oxidizing and dehydrating agent in various organic transformations. It can act as a hydrogen acceptor, facilitating dehydrogenation reactions, and has been applied in cyclization processes where controlled oxidation is required. Its ability to form stable adducts with phosphines and other nucleophiles has made it a valuable tool for activating otherwise unreactive functional groups, particularly in the synthesis of complex natural products and pharmaceuticals. In medicinal and natural product chemistry, diethyl azodicarboxylate has enabled the efficient construction of biologically active molecules by simplifying key bond-forming steps. The reagent’s compatibility with a broad range of functional groups allows sensitive substrates to be transformed without harsh acidic or basic conditions. As a result, it has been widely adopted in multi-step synthetic sequences where functional group tolerance and stereochemical control are essential. Diethyl azodicarboxylate has also influenced the development of alternative azo reagents and greener synthetic methods. Limitations related to its toxicity, explosiveness under certain conditions, and the generation of stoichiometric byproducts have motivated research into safer analogues and catalytic variants of reactions that traditionally relied on DEAD. Nonetheless, its historical importance remains clear, as many of these newer methodologies were designed by building on the mechanistic insights gained from its use. Overall, diethyl azodicarboxylate represents a landmark reagent in organic chemistry. From its discovery as a member of the azo ester family to its widespread application in substitution, oxidation, and stereoselective synthesis, it has profoundly shaped synthetic strategy. Its continued presence in the chemical literature reflects both its utility and its role in inspiring the development of more efficient and sustainable chemical transformations. References Mitsunobu O (1981) The use of diethyl azodicarboxylate and triphenylphosphine in synthesis and transformation of natural products. Synthesis 1981 1 1–28 DOI: 10.1055/s-1981-29317 Hughes DL (1992) The Mitsunobu reaction. Organic Reactions 42 335–656 DOI: 10.1002/0471264180.or042.02 Swamy KCK, Kumar NNB, Balaraman E, Kumar KVPP (2009) Mitsunobu and related reactions: advances and applications. Chemical Reviews 109 2551–2651 DOI: 10.1021/cr800278z |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Diethyl azodicarboxylate |