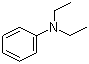
N,N-Diethylaniline is an organic compound belonging to the class of tertiary amines, characterized by the presence of two ethyl groups attached to a nitrogen atom, which is itself connected to a phenyl group. This compound has significant industrial and research applications, primarily due to its properties as a precursor for dyes, pigments, and pharmaceuticals. The discovery of N,N-diethylaniline dates back to the 19th century when chemists were exploring the synthesis and properties of aromatic amines.
The synthesis of N,N-diethylaniline can be traced to the work of German chemists in the 1870s, who began to investigate the alkylation of aniline derivatives. Aniline itself was first isolated in 1826 from coal tar by the chemist William Henry Perkin. Subsequent studies demonstrated that aniline could undergo various reactions to form substituted anilines, including N,N-diethylaniline. The compound was synthesized through the reaction of aniline with ethyl bromide in the presence of a base, such as sodium hydroxide, facilitating the introduction of the ethyl groups.
N,N-Diethylaniline is most notably used as a key intermediate in the production of azo dyes. These dyes are widely employed in the textile industry for their vibrant colors and excellent colorfastness properties. The synthesis of azo dyes involves the diazotization of aniline followed by coupling reactions, where N,N-diethylaniline serves as a crucial component. The presence of the ethyl groups enhances the solubility and reactivity of the compound, allowing for the formation of a variety of colored azo compounds that can be used to dye fabrics and other materials.
In addition to its role in dye manufacturing, N,N-diethylaniline is also utilized in the synthesis of other organic compounds, including pigments and pharmaceuticals. The compound can undergo various chemical reactions, such as acylation and oxidation, to yield derivatives with diverse functional properties. For instance, N,N-diethylaniline is involved in the synthesis of antioxidants, which are essential in preventing the degradation of polymers and other materials during processing and storage.
N,N-Diethylaniline has applications in the formulation of rubber and plastics, where it serves as a stabilizer and processing aid. Its ability to scavenge free radicals makes it valuable in improving the thermal stability and longevity of synthetic materials. In the cosmetics industry, N,N-diethylaniline can be found in hair dye formulations, where it contributes to the development of permanent color.
Safety and environmental concerns associated with N,N-diethylaniline have led to increased scrutiny of its use. The compound is considered hazardous, with potential health risks including skin irritation, respiratory issues, and its classification as a possible human carcinogen. Consequently, regulatory agencies have implemented guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of N,N-diethylaniline and its derivatives. Manufacturers are encouraged to explore safer alternatives and implement measures to mitigate exposure during production and application.
Research is ongoing to further understand the properties and potential applications of N,N-diethylaniline and its derivatives. Advances in synthetic chemistry and green chemistry principles are being applied to develop more sustainable methods for producing and utilizing this compound, aiming to minimize environmental impact while maximizing its industrial utility.
In summary, N,N-Diethylaniline is a versatile organic compound with a rich history in the synthesis of dyes, pigments, and various organic materials. Its discovery marked an important milestone in the study of aromatic amines, and its applications continue to evolve in response to the needs of various industries. Despite the challenges associated with its safety profile, ongoing research and innovation may pave the way for new uses and safer practices involving this important chemical substance.
|


















 GHS06;GHS08;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS08;GHS09 Danger Details