Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Jinxiang Chemical (Danyang) Products Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8681-9862 +86 13913839793 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com nancy-zong@hotmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| VanDeMark Chemical Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (716) 433-6764 | |||
 |
sales@vandemark.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1951 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| KS Laboratories Co., Ltd. | South Korea | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+82 (61) 753-9717 | |||
 |
semiyong@kslabo.co.kr | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Haorui Enterprises Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (755) 8296-0263 | |||
 |
lena@haorui.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1997 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2020 | ||||
| Nanjing Shunxiang Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (025) 8681-9868 | |||
 |
sales@jinchemical.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Changzhou Suntton Co., Ltd. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (914) 965-2077 +86 (519) 8513-6089 | |||
 |
luke.verdet@suntton.com lily.chen@suntton.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Oxime |
|---|---|
| Name | Dibenzyl azodicarboxylate |
| Synonyms | benzyl N-phenylmethoxycarbonyliminocarbamate |
| Molecular Structure | 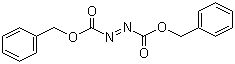 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H14N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 298.29 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2449-05-0 |
| EC Number | 219-508-0 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)COC(=O)N=NC(=O)OCC2=CC=CC=C2 |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 43 - 47 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 456.8±34.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 203.0±20.1 ºC (Calc.)*, 110 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.568 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dibenzyl azodicarboxylate is an organic azo compound belonging to the family of dialkyl and diaryl azodicarboxylates, which are best known for their role as reagents in organic synthesis. It consists of an azodicarboxylate core bearing two benzyl ester groups, giving the molecule a combination of aromatic substituents and a highly functionalized azo linkage. This structural motif imparts characteristic reactivity that has been exploited in laboratory and industrial chemistry. The development of azodicarboxylates is closely connected with the historical study of azo compounds and nitrogen nitrogen double bonds in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Early work on azo derivatives focused on their vivid colors and redox behavior, but systematic investigation of azodicarboxylates revealed their unique ability to participate in controlled redox processes and to activate alcohols and other functional groups. Dibenzyl azodicarboxylate emerged as one of several structurally related reagents designed to modify solubility, reactivity, and handling properties by variation of the ester substituents attached to the azodicarboxylate framework. In synthetic organic chemistry, dibenzyl azodicarboxylate is most strongly associated with its use as a component in Mitsunobu type reactions. In these transformations, azodicarboxylates react with phosphines to generate reactive intermediates that enable the substitution of alcohols with a wide range of nucleophiles under mild conditions. Compared with more commonly used dialkyl azodicarboxylates, the benzyl ester groups in dibenzyl azodicarboxylate influence the reaction profile by increasing molecular weight and lipophilicity and by allowing subsequent removal of protecting groups through hydrogenolysis. This property can be advantageous in multistep synthesis, where selective deprotection is required at a later stage. Beyond Mitsunobu chemistry, dibenzyl azodicarboxylate has been applied in other redox mediated transformations. The azo functional group can accept electrons, making the compound useful in reactions where controlled reduction is required. In some contexts, it serves as a precursor to hydrazine derivatives after reduction, which themselves are valuable intermediates in the construction of heterocycles and nitrogen rich frameworks. The benzyl protecting groups can then be removed under catalytic hydrogenation, yielding free carboxylic acid or hydrazine functionalities as needed. The compound has also found use in peptide and amino acid chemistry. The ability of azodicarboxylates to activate alcohols and related functional groups has been adapted to the modification of side chains and protecting groups in complex biomolecule synthesis. Dibenzyl azodicarboxylate offers compatibility with aromatic systems and protecting group strategies commonly used in this field, making it a useful alternative reagent when standard azodicarboxylates present limitations. From a practical standpoint, dibenzyl azodicarboxylate is typically encountered as a crystalline solid with good solubility in common organic solvents such as dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Its stability under normal storage conditions is adequate, although like many azo compounds it must be handled with care to avoid exposure to excessive heat or strong reducing agents. Standard laboratory precautions are sufficient for its safe use in synthetic procedures. Overall, dibenzyl azodicarboxylate represents a specialized but important member of the azodicarboxylate family. Its development reflects the broader evolution of reagent design in organic chemistry, where subtle changes in substituents are used to tune reactivity, selectivity, and downstream processing. Its applications in substitution reactions, redox chemistry, and complex molecule synthesis demonstrate its continuing relevance as a versatile tool in modern chemical research. References Zhu J, Lian Y, Guo J, Zhu S, Ma D (2008) General synthesis of C-glycosyl amino acids via proline-catalyzed direct electrophilic α-amination of C-glycosylalkyl aldehydes. Organic Letters 10 18 4117–4120 DOI: 10.1021/ol801685x Xu Y, Dolbier WR (2005) Total synthesis of LFA-1 antagonist BIRT-377 via organocatalytic asymmetric construction of a quaternary stereocenter. Organic Letters 7 3 473–476 DOI: 10.1021/ol047368b Zhu G, Chen Z, Jiang Q, Xiao D, Cao P,Zhang X (2004) Cu- and Pd-catalyzed asymmetric one-pot tandem addition-cyclization reaction of 2-(2',3'-alkadienyl)-β-keto esters, organic halides, and dibenzyl azodicarboxylate: an effective protocol for the enantioselective synthesis ofpyrazolidine derivatives. Organic Letters 6 13 2109–2112 DOI: 10.1021/ol0493498 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Dibenzyl azodicarboxylate |