Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Dalian Synco Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (411) 8363-5150 | |||
 |
daisy@syncochemie.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Suzhou J.M.S. Electronic Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 15995924277 | |||
 |
jms_jackie@foxmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Creative Peptides | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 624-4882 | |||
 |
info@creative-peptides.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Shanghai Hohance Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 3111-5312 | |||
 |
info@hohance.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Taizhou Tongxin Biopharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18652728585 | |||
 |
sales@allyrise.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2013 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Fatty acid |
|---|---|
| Name | (S)-(-)-2-Chloropropionic acid |
| Synonyms | 2-Chloropropanoic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 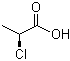 |
| Molecular Formula | C3H5ClO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 108.52 |
| CAS Registry Number | 29617-66-1 |
| EC Number | 411-150-5 |
| SMILES | C[C@@H](C(=O)O)Cl |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.27 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 4 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 189.0±13.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 220 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 101.7 ºC (Calc.)*, 107 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | soluble in water (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.441 (Calc.)*, 1.435 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H312-H302-H314 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Safety Description | S23;S26;S28;S36/37/39;S45 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2511 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(S)-(-)-2-Chloropropionic acid is a chiral halogenated carboxylic acid that has played a role in the historical development of stereochemistry and has found applications as a chemical intermediate in industrial and pharmaceutical synthesis. The compound consists of a three-carbon backbone bearing a carboxyl group and a chlorine atom at the second carbon, which is also the stereogenic center. The designation (S)-(-) indicates that the molecule has a specific absolute configuration and rotates plane-polarized light in the negative direction, properties that were central to its scientific significance. The discovery and characterization of 2-chloropropionic acid are closely connected to nineteenth-century research on optical activity and molecular asymmetry. During this period, chemists were investigating substituted lactic acids and related compounds to understand the relationship between chemical structure and optical rotation. When chlorine-substituted propionic acids were synthesized and resolved into optically active forms, they provided clear evidence that a single asymmetric carbon atom could give rise to enantiomeric molecules with distinct physical behavior. The isolation of the (S)-(-) enantiomer contributed to the broader acceptance of stereochemical theory and supported the concept of tetrahedral carbon proposed earlier in the century. In the early twentieth century, improved methods for resolving racemic mixtures and determining absolute configuration allowed chemists to study (S)-(-)-2-chloropropionic acid in greater detail. Its physical properties, such as melting point, boiling behavior, and optical rotation, were measured and compared with those of its enantiomer and related compounds. These studies helped establish systematic correlations between configuration, reactivity, and biological effects, reinforcing the importance of chirality in organic chemistry. From an applied perspective, (S)-(-)-2-chloropropionic acid has been primarily valued as an intermediate rather than as an end product. Its reactive carbon-chlorine bond makes it suitable for nucleophilic substitution reactions, enabling the introduction of a wide range of functional groups while retaining or controlling stereochemistry. This feature has been exploited in the synthesis of optically active compounds where the configuration at the carbon center is crucial for downstream properties. One significant area of application has been agrochemical synthesis. Chiral chloropropionic acid derivatives have been used as building blocks in the preparation of herbicides and other crop-protection agents. In such contexts, the specific stereochemistry can influence biological activity, environmental persistence, and toxicity. The availability of the (S)-(-) enantiomer has allowed chemists to study and optimize these effects, contributing to the development of more selective and efficient agricultural chemicals. (S)-(-)-2-Chloropropionic acid has also found use in pharmaceutical research and development. Chiral intermediates are essential in the synthesis of many drug candidates, as different enantiomers of a biologically active molecule can exhibit markedly different pharmacological profiles. By serving as a starting material for the construction of more complex chiral molecules, this compound has supported the exploration of structure-activity relationships and the production of enantiomerically enriched substances. In addition to its role in synthesis, the compound has continued to be of educational and scientific interest. It is frequently cited in discussions of stereochemical nomenclature, optical activity, and reaction mechanisms involving substitution at chiral centers. Its relatively simple structure makes it a useful example for illustrating how configuration can be preserved or inverted during chemical transformations. Overall, (S)-(-)-2-Chloropropionic acid represents a class of small chiral molecules whose importance extends beyond their immediate chemical properties. From its early contribution to the understanding of molecular asymmetry to its ongoing use as a versatile intermediate in applied chemistry, the compound has maintained relevance across both fundamental research and practical applications. References 2022. Synthesis, Conjugation, and Applications of Chiral Nanoparticles as Plasmonic Probes. Lecture Notes in Nanoscale Science and Technology. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-99491-4_14 2016. Functional Characterization of a Novel Marine Microbial Esterase and its Utilization in the Enantioselective Preparation of (R)-Methyl 2-Chloropropionate. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. DOI: 10.1007/s12010-016-2094-8 2015. A new l-haloacid dehalogenase from the Arctic psychrotrophic Pseudoalteromonas sp. BSW20308. Polar Biology. DOI: 10.1007/s00300-015-1674-3 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (S)-(-)-2-Chloropropionic acid |