Dihexyl ketone is an aliphatic ketone with the molecular formula C12H24O. Structurally, it consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) flanked by two hexyl (–C6H13) chains, giving it a symmetrical linear structure. The compound is typically a colorless liquid at room temperature, with low to moderate viscosity, a mild odor, and solubility in common organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and hydrocarbons, while being practically insoluble in water.
Dihexyl ketone is primarily used as a solvent and intermediate in organic synthesis. The carbonyl group is reactive toward nucleophiles, allowing the compound to participate in condensation reactions, reductions, and other transformations to produce alcohols, enolates, or substituted ketones. Its long alkyl chains confer hydrophobicity, making it useful in nonpolar reaction media or formulations requiring lipophilic components.
In industrial applications, dihexyl ketone can be used as a solvent in coatings, paints, and chemical processes where moderate polarity and low reactivity are required. Its chemical stability and low volatility relative to shorter-chain ketones make it suitable for formulations needing controlled evaporation rates and compatibility with hydrophobic materials.
Synthetically, dihexyl ketone can be prepared by the oxidation of dihexyl alcohols or by acylation reactions using hexyl derivatives and appropriate acylation reagents. Standard handling precautions include avoiding contact with strong oxidizing agents and open flames, as it is flammable.
Overall, dihexyl ketone is a versatile aliphatic ketone with applications as a solvent and chemical intermediate. Its combination of a reactive carbonyl group and long hydrophobic chains allows for use in organic synthesis, industrial formulations, and processes requiring a stable, moderately polar liquid.
References
2023. The LOTUS Initiative for Open Natural Products Research: frozen dataset union wikidata (with metadata). Zenodo.
DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.5794106
|









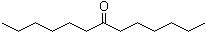
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details