Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Changzhou Xiali Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8878-3621 8849-4669 8872-1665 | |||
 |
xjq@xialichem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Zhejiang Huangyan Zhongxing Flavors & Fragrances Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (576) 8417-9161 | |||
 |
trade@zxff.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1993 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Jiangxi Time Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (794) 718-3888 718-3887 526-9970 +86 13867635890 | |||
 |
sales@groupchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Jiangxi Shengwei Aromatic Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (794) 525-9909 | |||
 |
hl.tz@163.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Ester >> Butyl ester compound |
|---|---|
| Name | tert-Butyl acetate |
| Synonyms | Acetic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester |
| Molecular Structure | 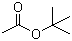 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 116.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 540-88-5 |
| EC Number | 208-760-7 |
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.863 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -62 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 98.0±8.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 97 - 98 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 15.6 ºC (Calc.)*, -15.6 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | water: Insoluble (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.397 (Calc.)*, 1.386 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS02 DangerGHS02 Details
GHS02 DangerGHS02 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H225 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P280-P303+P361+P353-P370+P378-P403+P235-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 1123 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
tert-Butyl acetate is an organic ester with the molecular formula C6H12O2. Structurally, it consists of a tert-butyl group (–C(CH3)3) linked to an acetyl group via an ester bond (–COO–). The molecule is a colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic fruity odor, low viscosity, and moderate volatility. It is soluble in most organic solvents but has limited solubility in water due to its bulky hydrophobic tert-butyl group. tert-Butyl acetate is primarily used as a solvent in coatings, paints, and inks due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of resins and polymers while evaporating at a controlled rate. Its high volatility and low polarity make it suitable for fast-drying formulations and industrial applications requiring rapid solvent removal. The compound is also employed as a reactive intermediate in organic synthesis. Its ester functionality allows for hydrolysis, transesterification, and nucleophilic substitution reactions, making it useful in the preparation of tert-butyl derivatives, acetates, and other functionalized compounds. In particular, tert-butyl esters are often used as protecting groups for carboxylic acids in multistep synthesis because they can be selectively removed under mildly acidic conditions. Synthetically, tert-butyl acetate is typically prepared by the esterification of acetic acid with tert-butanol in the presence of acid catalysts. Alternative methods include the reaction of tert-butyl alcohol with acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride. Handling requires standard precautions for flammable liquids, as it is highly combustible and can form explosive mixtures with air. Overall, tert-butyl acetate is a versatile ester widely used as a solvent and synthetic intermediate. Its combination of a bulky hydrophobic tert-butyl group and a reactive acetate moiety provides both chemical stability and reactivity, making it valuable in coatings, industrial applications, and organic synthesis. References 2025. Elucidation and Prevention of an Unexpected Methylamine Byproduct Formed During Trifluoroacetic Acid-Mediated Side Chain Deprotection of Azido-Containing Peptides. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics, 31(1). DOI: 10.1007/s10989-025-10726-x 2024. Structural aspects of HIV-1 integrase inhibitors: SAR studies and synthetic strategies. Molecular Diversity. DOI: 10.1007/s11030-024-11068-4 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for tert-Butyl acetate |