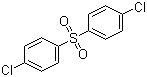
4,4'-Dichlorodiphenyl sulfone is an aromatic sulfone with the molecular formula C12H8Cl2O2S. Structurally, it consists of two phenyl rings connected through a sulfone group (–SO2–) at the para positions, with each phenyl ring also substituted at the 4-position with a chlorine atom. This configuration combines a rigid aromatic framework with strong electron-withdrawing substituents, resulting in high thermal stability and chemical resistance. The compound typically appears as a white crystalline solid, with low solubility in water and good solubility in polar aprotic organic solvents such as N-methylpyrrolidone, dimethylformamide, and dichlorobenzene.
4,4'-Dichlorodiphenyl sulfone is primarily used as a monomer in the synthesis of high-performance polymers, including polyarylene sulfones and polysulfones. Its para-substituted chloro groups serve as reactive sites for nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions with bisphenols or diamines, forming thermally stable, high-molecular-weight polymers. These polymers are valued for their excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and high thermal stability, making them suitable for applications in membranes, coatings, electrical components, and engineering plastics.
In addition, the compound can be used as an intermediate in the preparation of specialty chemicals and functionalized aromatic compounds. The chloro substituents allow for further substitution reactions, enabling the synthesis of modified sulfone-based monomers, crosslinkers, or ligands for advanced materials.
Synthetically, 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone is typically prepared via the sulfonation of chlorobenzene derivatives followed by oxidative coupling or condensation reactions under controlled conditions. Handling requires care due to its potential irritant properties and the need to avoid exposure to strong nucleophiles or high temperatures that could lead to unwanted side reactions.
Overall, 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone is a versatile aromatic sulfone with reactive para-chloro substituents and a rigid, thermally stable structure. Its combination of chemical reactivity, high thermal stability, and suitability for polymerization makes it an essential monomer and intermediate in the production of high-performance polymers and advanced materials.
References
2024. Aromatic Polysulfones: Synthesis, Properties, and Their Application. A Review. Polymer Science, Series D.
DOI: 10.1134/s1995421223700235
|




















 GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details