Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Capot Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-6718 +86 13336195806 | |||
 |
capotchem@gmail.com sales@capotchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Zhejiang Huangyan Zhongxing Flavors & Fragrances Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (576) 8417-9161 | |||
 |
trade@zxff.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1993 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Leping Zhongsheng Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (798) 670-2188 | |||
 |
sales@zhongshengchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Survival Technologies Pvt Ltd | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (22) 4212-8221 | |||
 |
info@survivaltechnologies.in | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Taicang Qianjing Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5364-5646 | |||
 |
sales@qjchem.com tcqxh@hotmail.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Ring Specialty Chemicals Inc. | Canada | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (416) 493-6870 | |||
 |
info@ringchemicals.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Phosphine ligand |
|---|---|
| Name | Triethyl phosphonoacetate |
| Synonyms | Diethyl ethoxycarbonylmethylphosphonate |
| Molecular Structure | 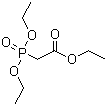 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17O5P |
| Molecular Weight | 224.19 |
| CAS Registry Number | 867-13-0 |
| EC Number | 212-757-6 |
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)CP(=O)(OCC)OCC |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.125 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -24 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 287.4±23.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 312.9 - 317.1 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 141.6±42.9 ºC (Calc.)*, 73.9 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.424 (Calc.)*, 1.432 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335-H411 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P273-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P391-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3082 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Triethyl phosphonoacetate is an organophosphorus ester with the molecular formula C8H17O5P. Structurally, it consists of a phosphonate group bearing three ethoxy substituents bonded to a methylene acetate moiety. This combination of a phosphonate ester and an activated ester functionality gives the compound distinctive reactivity, particularly in carbon–carbon bond-forming reactions. Triethyl phosphonoacetate is typically a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a mild odor. It is soluble in a wide range of organic solvents, including ethanol, ether, and chlorinated solvents, while being essentially insoluble in water. The compound was introduced into synthetic chemistry during the development of phosphonate-based reagents for olefination reactions. Its importance became firmly established with the advent of the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction, in which phosphonate-stabilized carbanions react with aldehydes or ketones to form alkenes. In this context, triethyl phosphonoacetate serves as a classic reagent for generating α,β-unsaturated esters with high selectivity. Compared with related phosphorus ylides, phosphonates such as triethyl phosphonoacetate often provide improved control over alkene geometry and milder reaction conditions. Triethyl phosphonoacetate is most widely applied in organic synthesis, particularly in the preparation of substituted acrylates and related unsaturated esters. Upon deprotonation at the methylene position adjacent to the phosphonate group, a stabilized carbanion is formed. This nucleophilic species readily reacts with carbonyl compounds, and subsequent elimination yields the desired alkene along with a phosphate byproduct. This transformation is extensively used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, fragrances, and fine chemicals, where conjugated ester systems serve as key intermediates. Beyond olefination chemistry, triethyl phosphonoacetate is also used as a precursor for other phosphonate derivatives and as an intermediate in multistep synthetic sequences. The ester functionality can be selectively hydrolyzed, reduced, or transformed into amides, allowing the molecule to act as a flexible synthon. In medicinal chemistry, derivatives obtained from triethyl phosphonoacetate have been incorporated into bioactive molecules and enzyme inhibitors, reflecting the versatility of the phosphonate motif in modulating biological activity. The compound is generally prepared by established methods such as the Arbuzov reaction, involving the reaction of triethyl phosphite with an appropriate haloacetate. This synthesis is reliable and scalable, making triethyl phosphonoacetate readily available for laboratory and industrial use. In handling, it is considered relatively stable under normal conditions, though it should be protected from moisture and strong bases when not in use. Standard laboratory precautions are sufficient, as the compound does not exhibit extreme toxicity or volatility compared with many other organophosphorus reagents. Overall, triethyl phosphonoacetate occupies a central position in modern synthetic organic chemistry. Its historical role in the development of phosphonate-based olefination methods, combined with its continued use as a practical and versatile reagent, underscores its importance. The ability of triethyl phosphonoacetate to efficiently construct carbon–carbon double bonds and to serve as a gateway to a wide range of functional molecules has made it a staple reagent in academic research and industrial chemical synthesis. References 2023. Synthesis and Biochemical Evaluation of Monocarboxylic GRB2 SH2 Domain Inhibitors. Methods in Molecular Biology. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3393-9_15 2022. Synthesis of a Respiratory Syncytial Virus Drug Candidate. Synfacts. DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1738396 2021. Applications of the Horner�Wadsworth�Emmons Olefination in Modern Natural Product Synthesis. Synthesis, 53(19). DOI: 10.1055/a-1493-6331 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Triethyl phosphonoacetate |