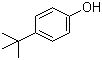
4-tert-Butylphenol is an aromatic phenol with the molecular formula C10H14O. Structurally, it consists of a phenol ring substituted at the para position with a tert-butyl group, giving it increased steric bulk compared with unsubstituted phenol. The hydroxyl group imparts nucleophilic and hydrogen-bonding properties, while the tert-butyl substituent enhances the molecule’s hydrophobicity and thermal stability. The compound is typically a colorless to pale yellow crystalline solid, soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and chloroform, but sparingly soluble in water.
4-tert-Butylphenol is primarily used as a monomer and intermediate in polymer and resin chemistry. Its phenolic hydroxyl group readily reacts with formaldehyde, epoxides, or acid chlorides to form phenolic resins, polyarylethers, and epoxy-based networks. The bulky tert-butyl group provides steric hindrance that can enhance the thermal stability, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance of the resulting polymers. These features make it valuable in adhesives, coatings, high-performance plastics, and electronic materials.
In addition to polymer applications, 4-tert-butylphenol is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of antioxidants, stabilizers, and fine chemicals. Its phenolic functionality allows further chemical modifications, such as alkylation, sulfonation, or esterification, enabling the production of derivatives with tailored properties for industrial or research applications.
The compound can be synthesized via alkylation of phenol with isobutylene under acidic conditions, typically using a Lewis acid catalyst. Handling precautions include avoiding inhalation, ingestion, and contact with skin or eyes, as phenolic compounds can be irritating, and working under appropriate ventilation due to its volatility and strong odor.
Overall, 4-tert-butylphenol is a versatile aromatic phenol combining a reactive hydroxyl group with a bulky hydrophobic tert-butyl substituent. Its properties make it a valuable building block for high-performance polymers, resins, antioxidants, and other functional chemical products.
References
2020. Multiresidue method for the determination of high production volume plastic additives in river waters. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(26).
DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-10118-2
2019. Au-polythionine nanocomposites: a novel mediator for bisphenol A dual-signal assay based on imprinted electrochemical sensor. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(15).
DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-01858-3
|




















 GHS05;GHS08;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS08;GHS09 Danger Details