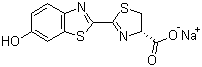
D-Luciferin sodium salt is the **sodium salt form of D-luciferin**, a naturally occurring substrate for the enzyme luciferase that produces bioluminescence. Structurally, D-luciferin contains a **benzothiazole ring** fused to a thiazoline ring, with a hydroxyl group at the 6-position of the benzothiazole and a carboxyl group at the 4-position of the thiazoline ring. The sodium salt form results from neutralization of the carboxylic acid group, increasing the compound’s solubility in aqueous solutions and making it more convenient for biological applications. Its molecular formula is C11H7N2NaO3S.
D-Luciferin and its sodium salt are primarily used as **bioluminescent substrates** in conjunction with luciferase enzymes. When D-luciferin is oxidized by luciferase in the presence of ATP and oxygen, it undergoes a chemical reaction that results in **emission of visible light**. This property makes it a central tool for non-invasive imaging in molecular and cellular biology, enabling researchers to monitor **gene expression, cell viability, and biochemical processes** in live cells, tissues, and whole organisms.
The sodium salt form is especially useful in experimental setups requiring **aqueous solutions**, such as in vitro enzymatic assays, live-cell imaging, or in vivo imaging of small animals. Its enhanced solubility allows for precise dosing, uniform distribution, and efficient interaction with luciferase, improving the sensitivity and reproducibility of bioluminescent measurements.
Synthetically, D-luciferin can be prepared from benzothiazole derivatives and cysteine through cyclization reactions that generate the thiazoline ring and install the carboxyl group. Conversion to the sodium salt is achieved by neutralizing the carboxylic acid group with sodium hydroxide or other suitable bases. This chemical modification does not interfere with the core structure responsible for enzymatic recognition and light emission.
Applications of D-luciferin sodium salt extend across **biochemistry, molecular biology, and imaging research**. In molecular biology, it is used as a reporter substrate for luciferase in assays measuring promoter activity or gene expression. In in vivo imaging, it enables the tracking of cells or organisms labeled with luciferase, facilitating studies in cancer research, infectious disease, and gene therapy. The compound’s biocompatibility, high quantum yield, and stability in aqueous media make it a widely adopted standard for bioluminescent imaging.
Overall, D-luciferin sodium salt is a versatile and essential reagent in bioluminescence research. Its sodium salt form combines the photophysical properties of D-luciferin with enhanced solubility, allowing precise and reproducible use in enzymatic assays and imaging applications. Its structural features, including the benzothiazole-thiazoline core, hydroxyl group, and carboxylate moiety, are critical for luciferase recognition and efficient light emission, making it a foundational tool in the study of biochemical and cellular processes.
References
2023. Suppression of TNBC metastasis by doxazosin, a novel dual inhibitor of c-MET/EGFR. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 42(1).
DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02866-z
2024. SorLA restricts TNFα release from microglia to shape a glioma-supportive brain microenvironment. EMBO Reports.
DOI: 10.1038/s44319-024-00117-6
|




















 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details