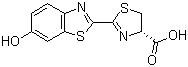
D-Luciferin is an heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C11H8N2O3S. Structurally, it consists of a benzothiazole ring fused to a thiazoline ring, with a hydroxyl group at the 6-position of the benzothiazole and a carboxylic acid at the 4-position of the thiazoline ring. The molecule exists in the naturally occurring D-enantiomer, which is the biologically active form recognized by luciferase enzymes in bioluminescent organisms. D-Luciferin is typically a pale yellow solid, soluble in aqueous and polar organic solvents under appropriate conditions.
D-Luciferin is best known as the substrate for luciferase-catalyzed bioluminescence. In the presence of luciferase, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and oxygen, D-Luciferin undergoes oxidation to produce light. This reaction forms the basis of bioluminescence in fireflies and other bioluminescent organisms and is widely exploited in molecular and cellular biology as a reporter system. The light emission is highly sensitive and can be quantified to monitor gene expression, cell viability, and biochemical processes in vitro and in vivo.
The compound is also used extensively in bioluminescence imaging applications. In live cells, tissues, and whole organisms, D-Luciferin enables non-invasive imaging of biological processes. Modifications of luciferin, such as creating derivatives with altered substituents, can tune emission wavelength, improve tissue penetration, or optimize signal stability for research purposes.
Synthetically, D-Luciferin can be prepared by condensation of appropriate benzothiazole derivatives with cysteine, forming the thiazoline ring and introducing the carboxylic acid group. The D-enantiomer is obtained using the corresponding enantiomer of cysteine, ensuring compatibility with luciferase. Handling requires standard precautions for heterocyclic compounds, and solutions are typically protected from light to prevent photodegradation.
Overall, D-Luciferin is a versatile and essential compound in biochemistry and molecular biology. Its benzothiazole-thiazoline core, hydroxyl group, and stereochemically defined carboxylate moiety are critical for enzymatic recognition and light emission, making it a central tool in bioluminescence assays, imaging studies, and biochemical research.
References
2020. Rapid and simple screening of the apoptotic compounds based on Hsp70 inhibition using luciferase as an intracellular reporter. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 412(3).
DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-02220-3
2021. Curbing gastrointestinal infections by defensin fragment modifications without harming commensal microbiota. Communications Biology, 4(1).
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01582-0
2021. A nanoemulsion/micelles mixed nanosystem for the oral administration of hydrophobically modified insulin. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 11(3).
DOI: 10.1007/s13346-021-00920-x
|



















 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details