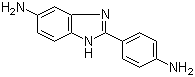
2-(4-Aminophenyl)-1H-benzimidazol-5-amine is an aromatic diamine with the molecular formula C13H11N3. Structurally, it consists of a benzimidazole core substituted at the 2-position with a 4-aminophenyl group and at the 5-position of the benzimidazole ring with an amino group. This arrangement provides two nucleophilic amino groups attached to a rigid, fused heteroaromatic system, combining high reactivity with structural rigidity. The compound typically appears as a pale yellow solid, soluble in polar organic solvents such as dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, and ethanol, but poorly soluble in water.
The compound is primarily used as a building block in polymer and materials chemistry. The amino groups can undergo condensation reactions with dianhydrides, diacid chlorides, or aldehydes to form polyimides, polyamides, Schiff bases, or other crosslinked networks. The fused benzimidazole structure contributes thermal stability, rigidity, and potential for hydrogen bonding, which is advantageous for designing high-performance polymers and materials with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
In addition to polymer synthesis, 2-(4-aminophenyl)-1H-benzimidazol-5-amine is used in the preparation of functional organic molecules and dyes. The aromatic amino groups allow for further functionalization via acylation, sulfonation, or other electrophilic substitutions, enabling the design of molecules with tailored optical, electronic, or chemical properties.
Synthetically, the compound can be prepared by the condensation of o-phenylenediamine derivatives with appropriate carboxylic acids or aldehydes to form the benzimidazole core, followed by selective introduction of the 4-aminophenyl substituent and amino group at the 5-position. Purification typically involves recrystallization or chromatographic techniques to ensure high purity suitable for polymerization or functionalization.
Overall, 2-(4-aminophenyl)-1H-benzimidazol-5-amine is a versatile diamine featuring a rigid heteroaromatic core with two reactive amino groups. Its combination of nucleophilicity, structural rigidity, and potential for further functionalization makes it valuable for high-performance polymers, functional materials, and advanced organic synthesis applications.
References
2022. Preparation of High-performance Polyimide Fibers with Wholly Rigid Structures Containing Benzobisoxazole Moieties. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 40(4).
DOI: 10.1007/s10118-022-2666-8
|





















 GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details